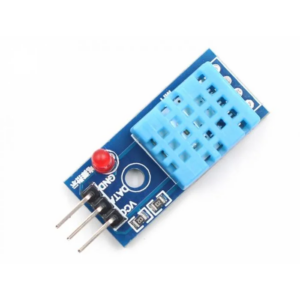
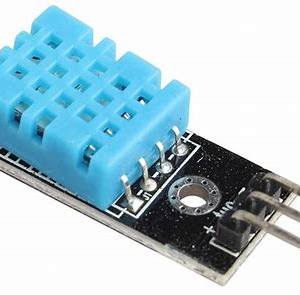
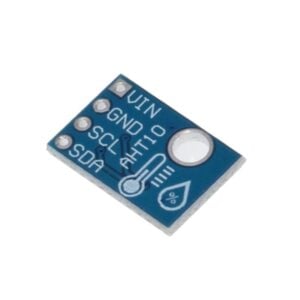
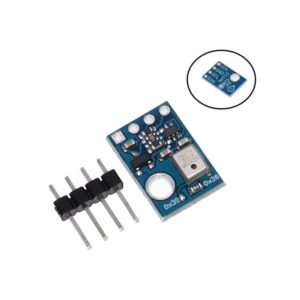
A temperature sensor is an electronic device that measures the temperature of its environment and converts the input data into electronic signals to record, monitor, or signal temperature changes. There are several different types of temperature sensors available:
1. Thermocouples: These are the most commonly used type of temperature sensor. Thermocouples are self-powered, require no excitation, can operate over a wide temperature range, and have quick response times. They work by joining two dissimilar metal wires together, creating a voltage difference due to the Seebeck Effect. Different types of thermocouples are made from various materials, allowing for different temperature ranges and sensitivities.
2. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs): RTDs rely on the change in resistance of a metal as the temperature changes. They offer high accuracy and stability over a wide temperature range. RTDs are commonly used in industrial and scientific applications.
3. Thermistors: Thermistors are widely used in human thermometers. Their resistance changes predictably with temperature variations. The resistance of a thermistor decreases with increasing temperature, making them suitable for precise temperature measurements.
4. Semiconductor-Based Sensors: These sensors use integrated circuits (ICs) to measure temperature. They are commonly found in consumer electronics and offer good accuracy and responsiveness.
Each type of sensor has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on factors such as measurement requirements, cost, and application specifics.
W1209 12V Digital Temperature Controller Module With Display and NTC Temperature Sensor Standard Quality
SKU: AI0478W1209 12V Digital Temperature Controller Module With Display and NTC Temperature Sensor
SKU: AI0022DS18B20 Water Proof Temperature Sensor Probe-1m
SKU: AI0317XH-W3001 AC 220V 1500W Digital Microcomputer Thermostat Switch
SKU: AI01533PIN Flame Sensor Infrared Receiver Ignition Source Detection Module
SKU: AI0143Analog Temperature Sensor Module
SKU: AI0202DHT-11 Temperature And Humidity Sensor Module
SKU: AI0070STC-1000 AC220V Digital Temperature Controlled Thermostat Switch
SKU: AI0483KSD9700 250V 5A 150° C Plastic Thermostatic Temperature Switch NC
SKU: AI0291Original DHT22 Digital Temperature and Humidity Sensor
SKU: AI0087XH-M452 Temperature and Humidity Controller Module
SKU: AI0487DHT-11 Digital Temperature And Humidity Sensor
SKU: AI0312Temperature and Humidity Sensor Model AHT20
SKU: AI0494LCD Electronic Fish Tank Water Detector Thermometer
SKU: AI0492DHT11 Temperature And Humidity Sensor Module with LED
SKU: AI33553 Pin NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor Module
SKU: AI0495XH-W3001 DC 12V 120W Digital Microcomputer Thermostat Switch
SKU: AI0488MAX6675 Thermocouple Sensor Module
SKU: AI0469DHT-11 Temperature And Humidity Sensor Module with cable
SKU: AI0870AM2305B Digital Temperature and Humidity Sensor
SKU: AI0449HTU21D Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module
SKU: AI0574AHT21B Temperature and Humidity Sensor Temperature
SKU: AI0739DHT22 Digital Temperature and Humidity Sensor-Standard Quality
SKU: AI0433AHT25 Integrated Temperature And Humidity Sensor
SKU: AI0843XH-W1219 12V Digital Red and Green Display Temperature Controller Module With NTC Waterproof Temperature Sensor
SKU: AI0259DHT20 SIP Packaged Temperature and Humidity Sensor
SKU: AI05400 to 600 °C Surface Thermocouple K Type High Temperature Resistance Probe
SKU: AI2097KSD301 Normal Close NC Temperature Controlled Switch Thermostat
SKU: AI2823HTC-1 High Precision Large Screen Electronic Indoor Temperature, Humidity Thermometer with Clock Alarm
SKU: AI0486MAX6675 Module with K Type Thermocouple Sensor
SKU: AI0493AHT10 High Precision Digital Temperature And Humidity Measurement Module
SKU: AI2112DHT11 Digital Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor Module
SKU: AI5202DHT22 – Temperature and Humidity Sensor Module(with cable)
SKU: AI0340MAX31865 PT100-PT1000 RTD Platinum Resistance Temperature Detector Module
SKU: AI2529B3950 10K NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor 5*25mm with XH2.54 Connector with 0.5 Meter Cable
SKU: AI23214PIN NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensor Module
SKU: AI0504Product categories
- Show All Categories
- 3D Printers and Parts (140)
- Batteries & Chargers and Accessories (560)
- Clearance Sale (0)
- Development Boards (306)
- DIY Learning and Robot Kits (44)
- Drone Parts (595)
- EBike parts (141)
- Electronic Components (657)
- Electronic Modules and Displays (972)
- IoT and Wireless (366)
- Mechanical Parts and Workbench Tools (192)
- Motors & Drivers & Pumps & Actuators (522)
- Refurbished & Partial Working (0)
- Sensors Modules (542)
- Services (0)
- Uncategorized (90)
- Sensors Modules (542)
- Biometric/ECG/EMG Sensor (18)
- Current and Voltage Sensor (28)
- Distance Sensor (7)
- Environmental Sensors (14)
- Flame Sensor (1)
- Gas and Dust Sensor (41)
- Hall Sensor (8)
- IMU, Accelerometer, Magnetometer & Gyroscope (19)
- LiDAR Sensor (4)
- Light/color Sensor (21)
- Line Sensor (5)
- Load / Pressure / Force / Flex Sensor (22)
- Other Sensors (7)
- PIR / IR and Optical Sensor (43)
- Proximity Sensor (14)
- RFID card (2)
- RFID card, Tags & Reader (15)
- Rotary Encoder (13)
- Sensor Kits (1)
- Sound Sensor (11)
- Temperature & Humidity Sensor (84)
- Thermoelectric Peltier Elements (47)
- Ultrasonic Sensors and Modules (24)
- Vibration/Tilt Sensor and Modules (20)
- Water TDS, pH, Flow, Level and Pressure Sensor (75)