A distance sensor is a reliable tool for various applications, providing accurate and fast measurements, precise positioning, and the ability to detect an extensive range of materials. Let’s explore the different types of distance sensors available:
1. Ultrasonic Sensor: Also known as the Sonar sensor, the ultrasonic sensor emits high-frequency sound waves toward a target object. When the object reflects these waves back to the sensor, a timer starts. By calculating the time taken for the wave’s return against the speed of sound, the sensor determines the distance traveled.
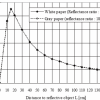
2. IR (Infrared) Triangulation Sensor: This type of sensor uses infrared light to measure distances. It works by emitting IR light and analyzing how it changes when reflected by an object.
3. Laser Distance Sensor (LIDAR): LIDAR sensors use laser beams to measure distances accurately. They are commonly used in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and mapping applications.
4. VCSEL (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser) Sensor: VCSEL sensors offer high resolution and low cost. They use an I2C interface and are suitable for various applications.
Each type has its advantages and drawbacks. For example:
– Ultrasonic sensors are reliable, low-cost, and easy to set up but have lower resolution and slower refresh rates.
– LIDAR sensors have excellent range but can be expensive and have a large footprint.
– VCSEL sensors provide good resolution and low cost but have a limited maximum range.
Applications of distance sensors include measuring distances, robot gripper placement, palletizing tasks, coil diameter measurement, and component detection.
Sharp Distance Measuring Sensor unit 10 to 80cm – GP2Y0A21YK0F
SKU: AI0362CJMCU-531 VL53L1X Laser Ranging Flight Time Sensor Module Distance 400cm Measurement Extension Board
SKU: AI2996MPU-6050 Module GY-521 Module with Soldering
SKU: AI3562SHARP Distance Measuring Sensor unit 100 to 550 cm -GP2Y0A710K0F with Cable
SKU: AI2468SHARP Distance Measuring Sensor unit 20 to 150 cm – GP2Y0A02YK0F
SKU: AI2466SHARP IR Distance Measuring Sensor Unit 4 ~ 30 cm With Cable-[GP2Y0A41SK0F]
SKU: AI2467Bosch GLM 50-23 G 50M Range Laser Distance Meter with Color Backlit Display
SKU: AI1629Product categories
- Show All Categories
- 3D Printers and Parts (140)
- Batteries & Chargers and Accessories (560)
- Clearance Sale (0)
- Development Boards (306)
- DIY Learning and Robot Kits (44)
- Drone Parts (595)
- EBike parts (141)
- Electronic Components (657)
- Electronic Modules and Displays (972)
- IoT and Wireless (366)
- Mechanical Parts and Workbench Tools (192)
- Motors & Drivers & Pumps & Actuators (522)
- Refurbished & Partial Working (0)
- Sensors Modules (542)
- Services (0)
- Uncategorized (90)
- Sensors Modules (542)
- Biometric/ECG/EMG Sensor (18)
- Current and Voltage Sensor (28)
- Distance Sensor (7)
- Environmental Sensors (14)
- Flame Sensor (1)
- Gas and Dust Sensor (41)
- Hall Sensor (8)
- IMU, Accelerometer, Magnetometer & Gyroscope (19)
- LiDAR Sensor (4)
- Light/color Sensor (21)
- Line Sensor (5)
- Load / Pressure / Force / Flex Sensor (22)
- Other Sensors (7)
- PIR / IR and Optical Sensor (43)
- Proximity Sensor (14)
- RFID card (2)
- RFID card, Tags & Reader (15)
- Rotary Encoder (13)
- Sensor Kits (1)
- Sound Sensor (11)
- Temperature & Humidity Sensor (84)
- Thermoelectric Peltier Elements (47)
- Ultrasonic Sensors and Modules (24)
- Vibration/Tilt Sensor and Modules (20)
- Water TDS, pH, Flow, Level and Pressure Sensor (75)









![SHARP IR Distance Measuring Sensor Unit 4 ~ 30 cm With Cable-[GP2Y0A41SK0F]](https://zbotic.in/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/443506-ir-distance-sensor-sharp-gp2y0a41sk0f-7467-300x300.jpg)

